Three-dimensional scanning, commonly referred to as 3D scanning, is a rapidly developing technology that involves capturing the physical shape and characteristics of objects or environments using a range of techniques, such as structured light, laser, or photogrammetry.
This process involves the use of a 3D scanner to collect and convert data on the object’s geometry, color, and texture into a digital format that can be used for a wide range of applications, including quality control, reverse engineering, prototyping, digital preservation, and more.
3D scanning allows for a precise and accurate representation of the object, enabling thorough analysis and manipulation, as well as improved design and manufacture. With the continuous development of this technology, 3D scanning has become more accessible and affordable, making it an increasingly essential tool in various industries, such as healthcare, automotive, architecture, and entertainment, among others.
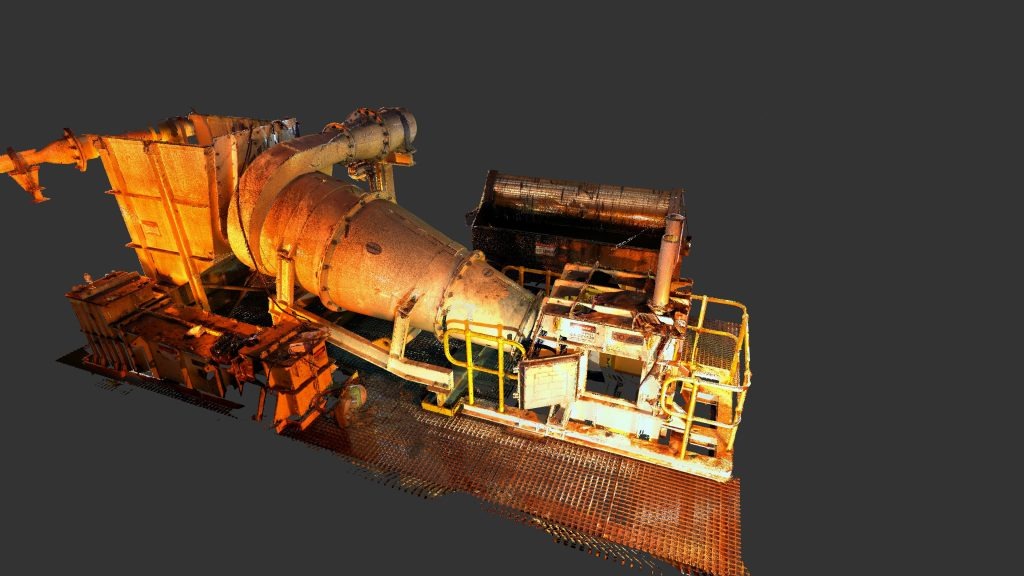
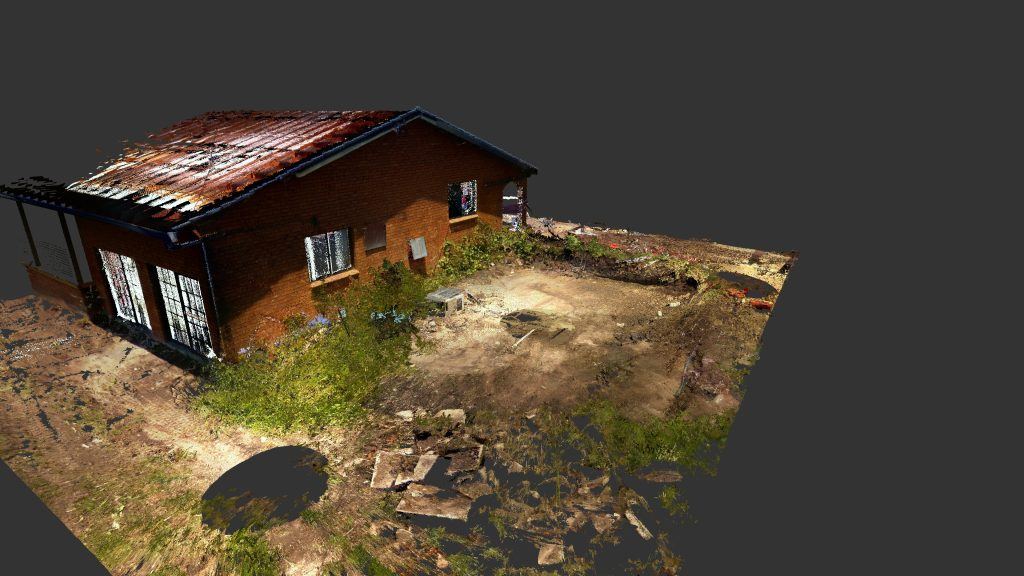


If you would like to engage Motion Group to carry out your 3d Scanning needs, then please fill out the form below or call 0240673718.

